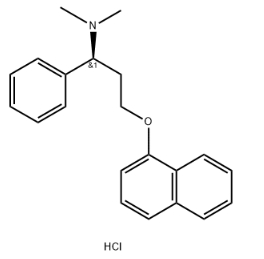
Chemical Name:
Dapoxetine hydrochloride is chemically known as (S)-N,N-dimethyl-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)-phenylpropanamine hydrochloride.
Pharmacology:
Dapoxetine hydrochloride shares similar pharmacological activity with other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Initially developed as an antidepressant, dapoxetine differs from traditional SSRIs in its pharmacokinetics—exhibiting rapid oral absorption, short half-life, and fast elimination. These properties make it suitable for on-demand use in the treatment of premature ejaculation (PE).
Clinical Use:
Dapoxetine hydrochloride is a short-acting oral SSRI used to treat premature ejaculation in men. Developed by Eli Lilly, it was first launched in Europe in 2009 under the brand name Priligy.
Physical Properties:
Dapoxetine hydrochloride is a white to off-white powder. It is readily soluble in methanol and ethanol, slightly soluble in 1,2-dichloroethane, and almost insoluble in water. As a BCS Class II compound, its poor solubility is a key factor contributing to variability in clinical efficacy. Dapoxetine hydrochloride exists in multiple polymorphic forms, which can exhibit significant differences in solubility and may undergo phase transformation.
Adverse Effects:
During treatment, dapoxetine tablets may cause side effects such as headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and diarrhea. These adverse effects are typically mild and transient, posing no serious threat to patients and usually resolving quickly.